2025
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Complex Multi-modal Diagnosis in Dentistry
Zhenyang Cai, Jiaming Zhang, Junjie Zhao, Ziyi Zeng, Yanchao Li, Jingyi Liang, Junying Chen, Yunjin Yang, Jiajun You, Shuzhi Deng, Tongfei Wang, Wanting Chen, Chunxiu Hao, Ruiqi Xie, Zhenwei Wen, Xiangyi Feng, Zou Ting, Jin Zou Lin, Jianquan Li, Liangyi Chen, Junwen Wang, Shan Jiang, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
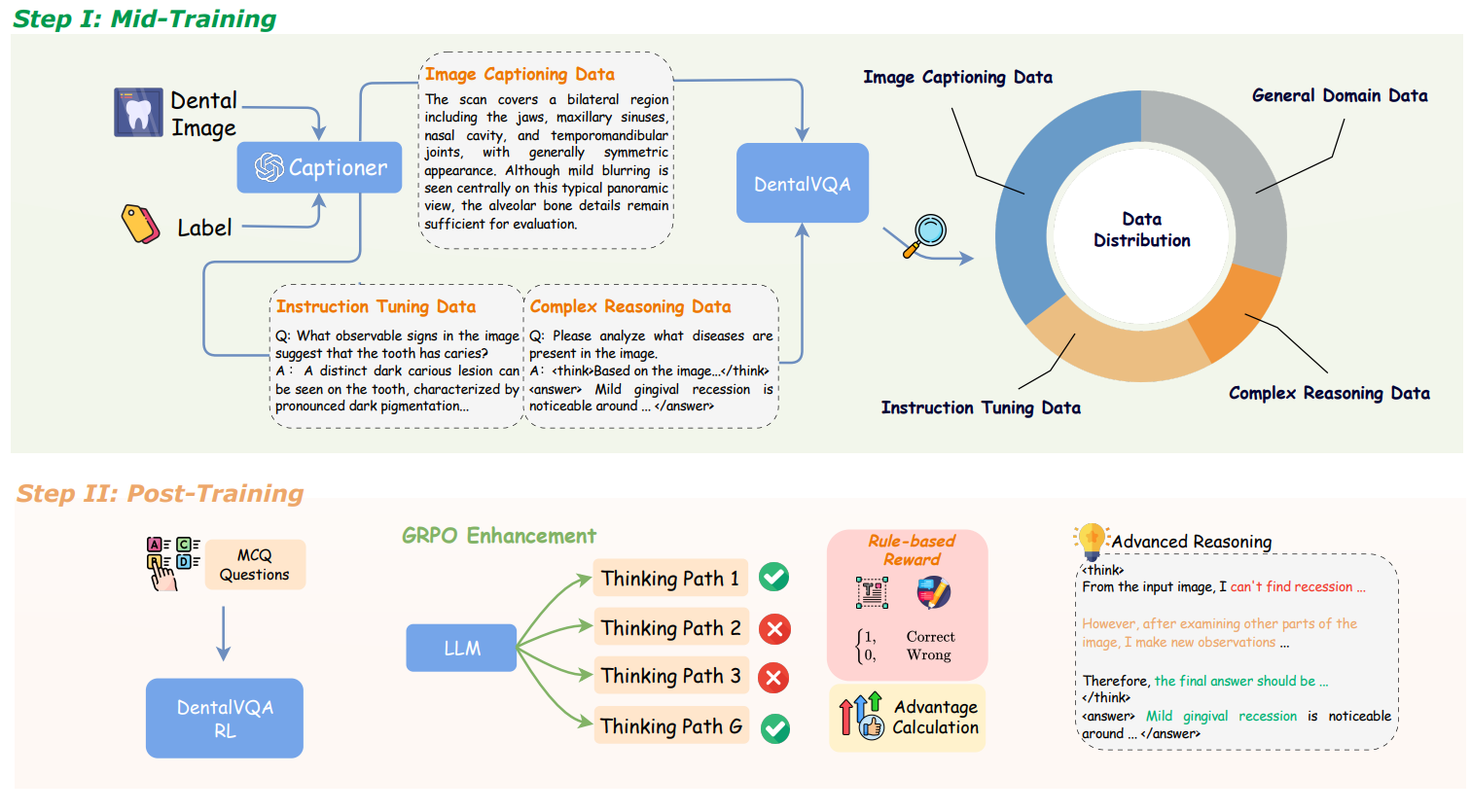
This work presents DentalGPT, a 7B dental-specific multimodal model developed through high-quality domain data and staged training. Using DentalVQA, the largest annotated dental image dataset, together with GRPO-based post-training, the model achieves state-of-the-art results in dental disease classification and VQA, showing the effectiveness of targeted domain adaptation.
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Complex Multi-modal Diagnosis in Dentistry
Zhenyang Cai, Jiaming Zhang, Junjie Zhao, Ziyi Zeng, Yanchao Li, Jingyi Liang, Junying Chen, Yunjin Yang, Jiajun You, Shuzhi Deng, Tongfei Wang, Wanting Chen, Chunxiu Hao, Ruiqi Xie, Zhenwei Wen, Xiangyi Feng, Zou Ting, Jin Zou Lin, Jianquan Li, Liangyi Chen, Junwen Wang, Shan Jiang, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
This work presents DentalGPT, a 7B dental-specific multimodal model developed through high-quality domain data and staged training. Using DentalVQA, the largest annotated dental image dataset, together with GRPO-based post-training, the model achieves state-of-the-art results in dental disease classification and VQA, showing the effectiveness of targeted domain adaptation.
ShizhenGPT: Towards Multimodal LLMs for Traditional Chinese Medicine
Junying Chen, Zhenyang Cai, Zhiheng Liu, Yunjin Yang, Rongsheng Wang, Qingying Xiao, Xiangyi Feng, Zhan Su, Jing Guo, Xiang Wan, Guangjun Yu, Haizhou Li, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
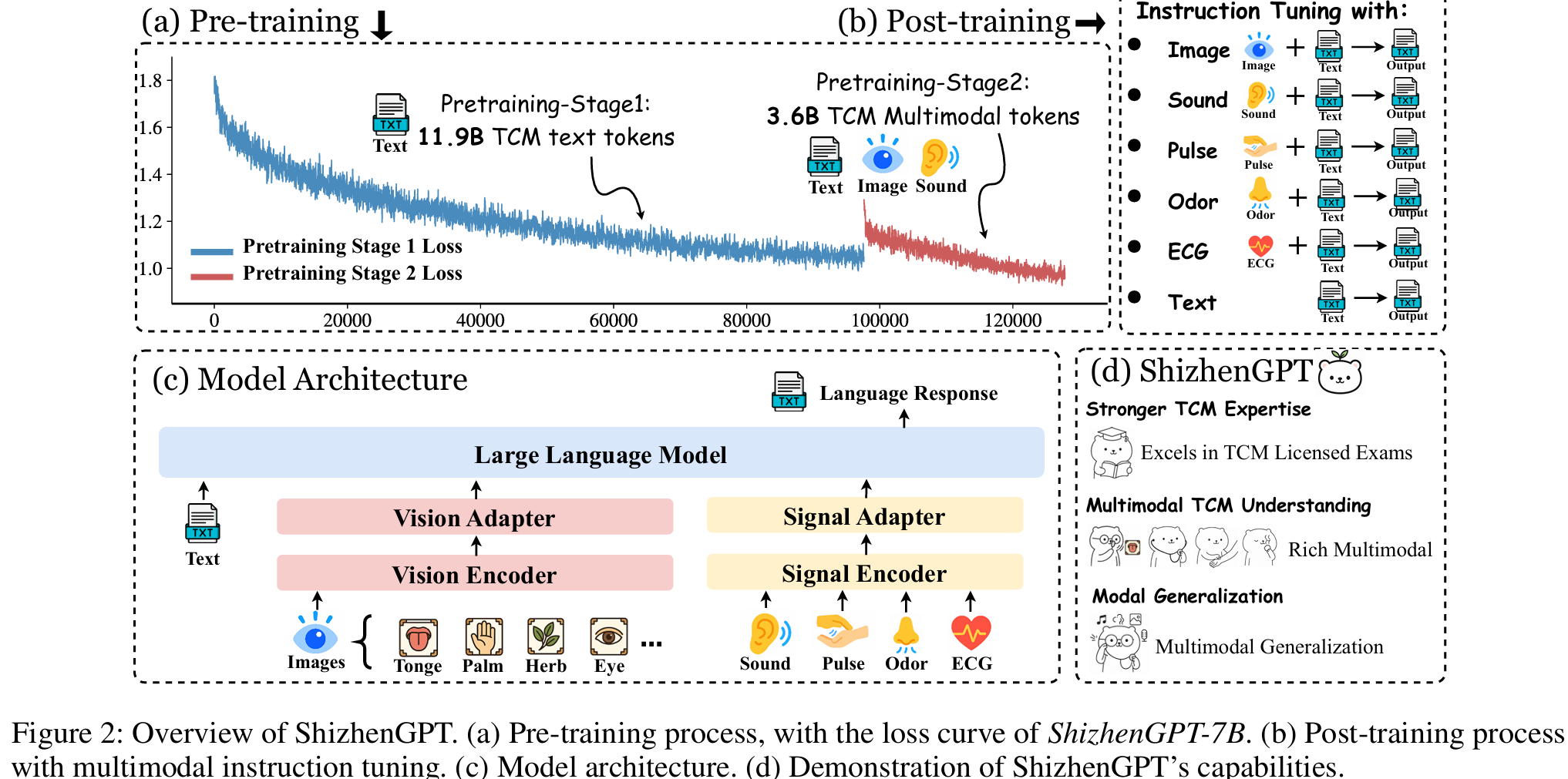
This work introduces ShizhenGPT, the first multimodal large language model for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), addressing data scarcity and the inherently multimodal nature of TCM diagnostics. We curate the largest TCM dataset to date (300GB+ across text, images, audio, and physiological signals) and evaluate the model using national TCM qualification exams and a new visual diagnosis benchmark. Experiments show that ShizhenGPT surpasses comparable LLMs and achieves state-of-the-art multimodal perception across pulse, smell, sound, and vision, paving the way for holistic TCM diagnostic intelligence.
ShizhenGPT: Towards Multimodal LLMs for Traditional Chinese Medicine
Junying Chen, Zhenyang Cai, Zhiheng Liu, Yunjin Yang, Rongsheng Wang, Qingying Xiao, Xiangyi Feng, Zhan Su, Jing Guo, Xiang Wan, Guangjun Yu, Haizhou Li, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
This work introduces ShizhenGPT, the first multimodal large language model for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), addressing data scarcity and the inherently multimodal nature of TCM diagnostics. We curate the largest TCM dataset to date (300GB+ across text, images, audio, and physiological signals) and evaluate the model using national TCM qualification exams and a new visual diagnosis benchmark. Experiments show that ShizhenGPT surpasses comparable LLMs and achieves state-of-the-art multimodal perception across pulse, smell, sound, and vision, paving the way for holistic TCM diagnostic intelligence.
MedGen: Unlocking Medical Video Generation by Scaling Granularly-annotated Medical Videos
Rongsheng Wang, Junying Chen, Ke Ji, Zhenyang Cai, Shunian Chen, Yunjin Yang, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
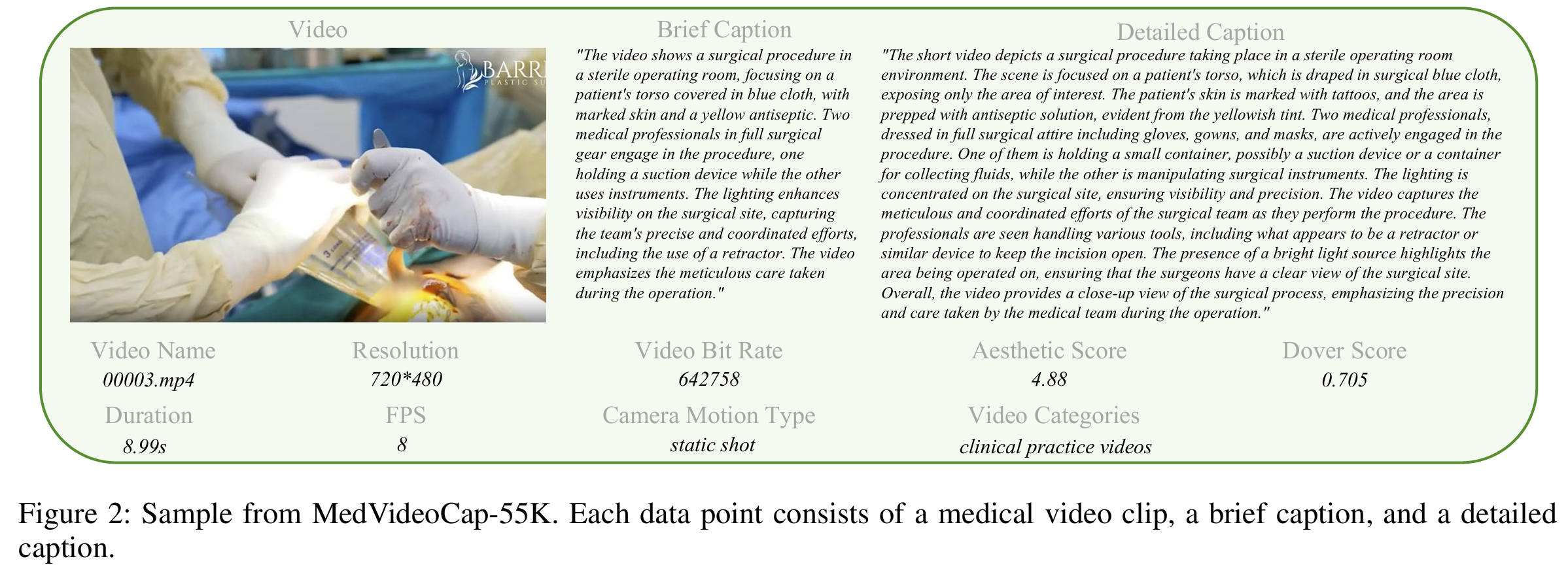
This work addresses the lack of domain-specific data for medical video generation by introducing MedVideoCap-55K, a large-scale, diverse, caption-rich dataset covering real clinical scenarios. Leveraging it, we develop MedGen, which delivers state-of-the-art visual fidelity and medical accuracy among open-source models, rivaling commercial systems.
MedGen: Unlocking Medical Video Generation by Scaling Granularly-annotated Medical Videos
Rongsheng Wang, Junying Chen, Ke Ji, Zhenyang Cai, Shunian Chen, Yunjin Yang, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
This work addresses the lack of domain-specific data for medical video generation by introducing MedVideoCap-55K, a large-scale, diverse, caption-rich dataset covering real clinical scenarios. Leveraging it, we develop MedGen, which delivers state-of-the-art visual fidelity and medical accuracy among open-source models, rivaling commercial systems.
ShareGPT-4o-Image: Aligning Multimodal Models with GPT-4o-Level Image Generation
Junying Chen, Zhenyang Cai, Pengcheng Chen, Shunian Chen, KeJi, Xidong Wang, Yunjin Yang, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
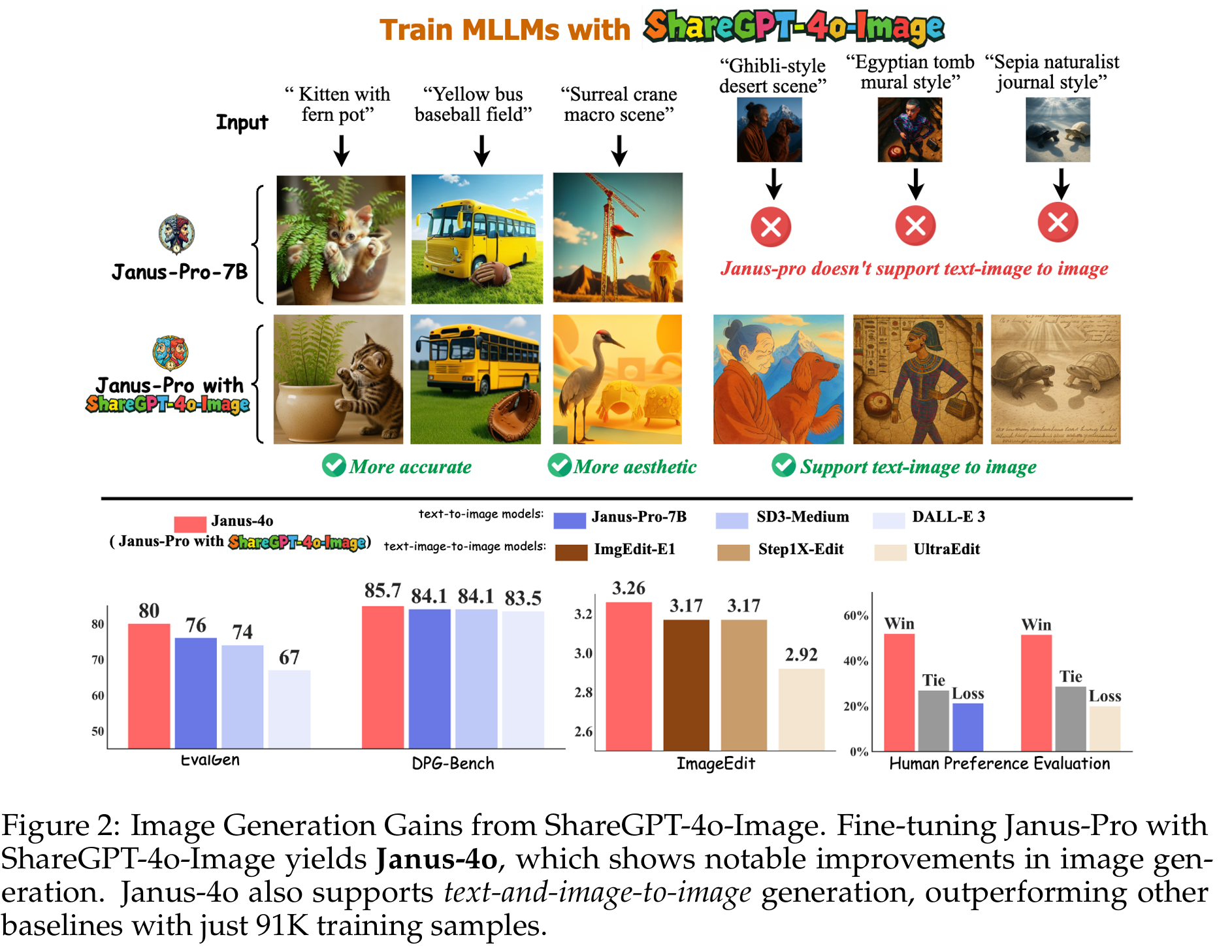
This work introduces ShareGPT-4o-Image, a 91K-sample synthetic dataset distilled from GPT-4o to enable open photorealistic, instruction-aligned image generation. Building on it, Janus-4o advances text-to-image quality over Janus-Pro and newly supports text-and-image-to-image generation, achieving strong performance with only six hours of training on 8×A800 GPUs.
ShareGPT-4o-Image: Aligning Multimodal Models with GPT-4o-Level Image Generation
Junying Chen, Zhenyang Cai, Pengcheng Chen, Shunian Chen, KeJi, Xidong Wang, Yunjin Yang, Benyou Wang
Under review. 2025
This work introduces ShareGPT-4o-Image, a 91K-sample synthetic dataset distilled from GPT-4o to enable open photorealistic, instruction-aligned image generation. Building on it, Janus-4o advances text-to-image quality over Janus-Pro and newly supports text-and-image-to-image generation, achieving strong performance with only six hours of training on 8×A800 GPUs.
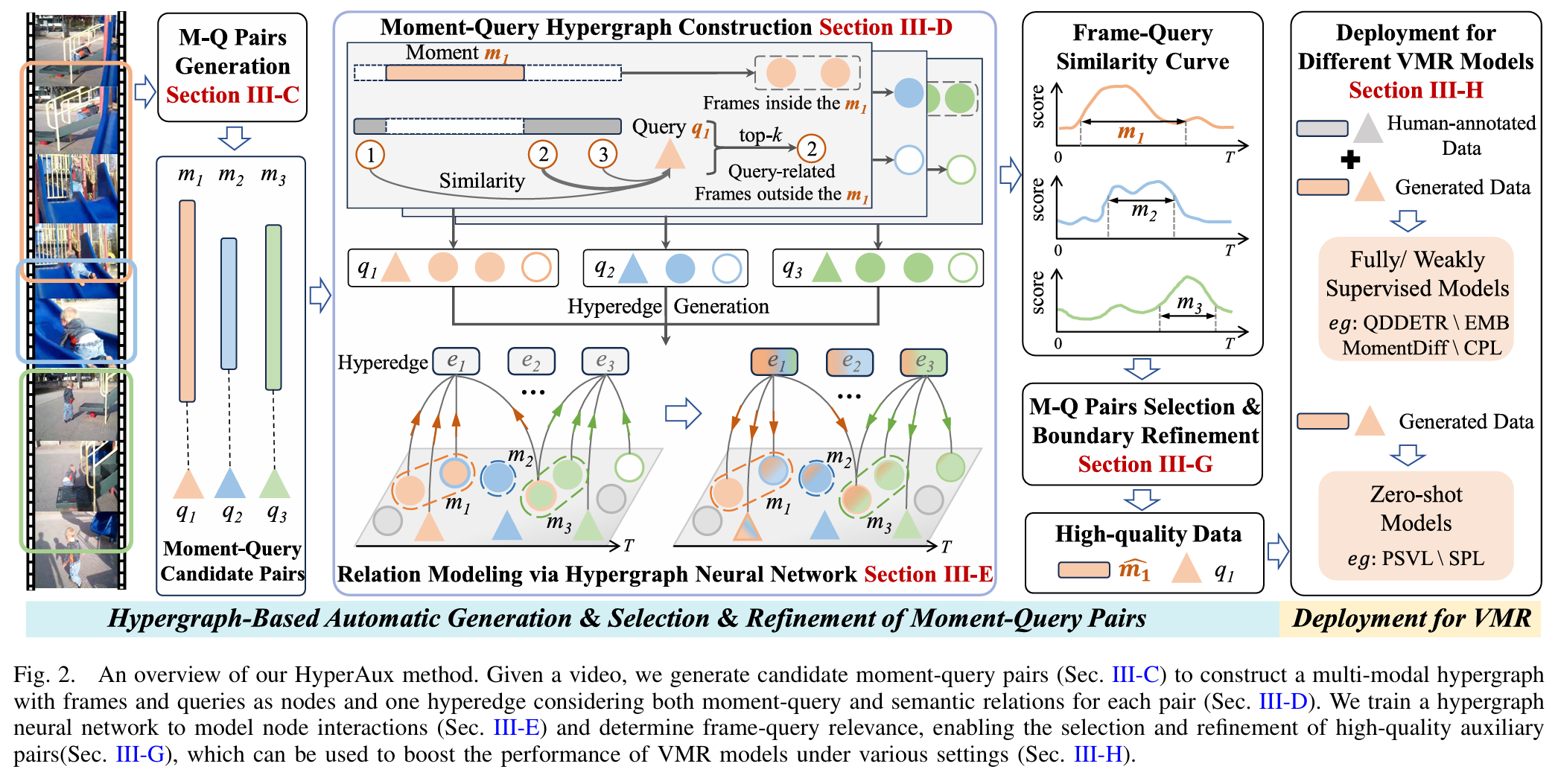
Improving Video Moment Retrieval by Auxiliary Moment-Query Pairs With Hyper-Interaction
Runhao Zeng, Yishen Zhuo, Jialiang Li, Yunjin Yang, Huisi Wu, Qi Chen, Xiping Hu, Victor C. M. Leung
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2025 Accepted
This work introduces HyperAux, a hypergraph-based framework that enriches video moment retrieval (VMR) training data by generating and selecting high-quality moment–query pairs. By modeling multi-modal hyper-interactions among frames and queries, HyperAux produces context-aware representations that refine moment boundaries and improve pair selection. Without requiring human annotations, it leverages semantic discrepancies inside and outside moments to guide training. The resulting auxiliary data boosts twelve VMR models across fully-supervised, weakly-supervised, and zero-shot settings on ActivityNet Captions, Charades-STA, and QVHighlights.
Improving Video Moment Retrieval by Auxiliary Moment-Query Pairs With Hyper-Interaction
Runhao Zeng, Yishen Zhuo, Jialiang Li, Yunjin Yang, Huisi Wu, Qi Chen, Xiping Hu, Victor C. M. Leung
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2025 Accepted
This work introduces HyperAux, a hypergraph-based framework that enriches video moment retrieval (VMR) training data by generating and selecting high-quality moment–query pairs. By modeling multi-modal hyper-interactions among frames and queries, HyperAux produces context-aware representations that refine moment boundaries and improve pair selection. Without requiring human annotations, it leverages semantic discrepancies inside and outside moments to guide training. The resulting auxiliary data boosts twelve VMR models across fully-supervised, weakly-supervised, and zero-shot settings on ActivityNet Captions, Charades-STA, and QVHighlights.